Substances in Cannabis
2625 Views |

Currently, there are 565 constituents of cannabis found, data from 2015. Divided into 3 main groups: cannabinoids, terpenes, flavonoids
cannabinoid group
There are more than 100 types of cannabinoids. As for plants, they are found only in cannabis. The cannabinoids derived from cannabis are called phytocannabinoids, not to be confused with man-made cannabinoids.
Many people may wonder if marijuana can create cannabinoids that are similar to those produced by the body. The answer is almost the same but can be used interchangeably. The chemical structure of phytocannabinoids from cannabis is similar to the chemical structure of the cannabinoids that the body produces for use in the body's functioning system known as Endocannabinoid System (ESC)
Endocannabinoid System is a system to maintain the balance of the body to work normally by controlling the operation of various systems such as whole nervous system, physical process, response to pain, appetite, digestion, mood, inflammation, immune system, sensory system, heart function, and others. These systems are controlled by the endocannabinoid system.
If the human body cannot produce cannabinoids or can build less. The body will have abnormal symptoms, various diseases may occur. The use of cannabinoids derived from cannabis to replace. Thus, it helps to treat and prevent diseases caused by cannabinoid deficiency. The expand of the working process of cannabinoids for readers is in the next article. Now let's move on to the topic of substances in the cannabinoid group first.
Cannabinoids are the important substances in cannabis. The most well-known and researched substances currently are THC, CBD, CBG, CBC, CBN. The most popular ones are delta 9, tetrahydrocannabinoids (THC), and cannabidiol (CBD)
The difference between THC and CBD
THC and CBD are very similar. In addition to being in the same group of cannabinoids, they also have the same atomic composition. THC and CBD are composed of 21 atoms of carbon, 30 atoms of hydrogen, and 2 atoms of oxygen. The difference is in the arrangement of the atoms and it’s resulting in different effects on internal body systems as well.
The obvious difference is that THC is a psychoactive substance, it causes the user to get drunk or "high" while CBD does not have a direct neurological effect causing the user to not be drunk. This is because they work differently on cannabinoid receptors in our bodies.
These cannabinoid receptors are naturally present in the human body. Cannabinoid receptors can be divided into two types: CB1 and CB2. CB1 cannabinoid receptors are located in the central nervous system while the cannabinoid CB2 receptor is located in the peripheral nervous system.
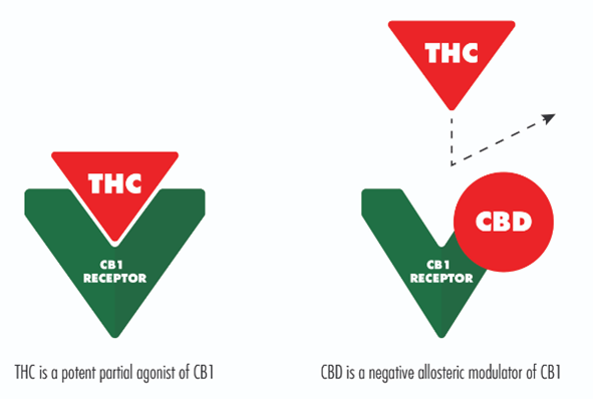
The CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the central nervous system that respond to THC that leading to a feeling high. Also, human enzymes are harder to break down THC than CBD, so the high can last for a certain amount of time as the amount of THC remains in the body.
The obvious difference between the two is the “feel” that occurs when they are exposed to both substances.
THC
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in appropriate doses will reduce pain, muscle spasms, and intestinal symptoms.
If you take it in high doses, it will cause drunkenness, palpitations, fainting, hallucinations, disrupt the chemical activity of the brain, distort perception, decision-making, and memory effect.
If you have taken in high doses continuously, it will cause resistance to Tolerance, causing the need to increase the dose to get the same effect and lead to addiction.
CBD
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a substance that has the effect of helping with motion sickness and solve mental symptoms from THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol). In addition, Cannabidiol (CBD) has been studied and researched on the use of CBD to control seizures and pain, but has not been found to cause drug resistance or addiction.
CBC
CBC is another non-psychoactive cannabinoid that, despite it’s discovered in the 1960s, but it has not been thoroughly studied. Some studies have suggested that CBC increases the pain-relieving properties of THC and may have more powerful anti-depressant properties than CBD. It’s also associated with treating nausea and vomiting. It is a matter of further medical study.
CBG
CBG is a very small amount of cannabinoid but it is useful for treating problems related to glaucoma, depression, and pain relief. CBD is a chemical precursor to other cannabinoids such as CBD and THC as it undergoes a chemical transformation during plant growth. For this reason, there is often an inverse relationship between high CBG and low THC levels. CBG is not intoxicating.
CBG has been found to be effective in treating glaucoma as it lowers intraocular pressure. CBG is a medicine for dilates blood vessels and it has a protective effect on the nervous system. In experiments, CBG was shown to be effective at reducing the inflammatory nature of inflammatory bowel disease and protecting neurons in mice with Huntington's disease, which is characterized by neuronal degeneration in the brain. There is also preliminary research indicating that CBG may be able to inhibit the growth of colorectal cancer cells.
CBN
The main compound that works as a sleep aid is cannabinol in small proportions and less readily available than CBD or THC. Although it was one of the first cannabinoids to be discovered, CBN is produced when THC is oxidized, which is why dried cannabis flowers exposed to oxygen can be a good source for CBN extraction. In addition to being an effective sleep aid, CBN also combines with CBD and THC for its powerful anti-inflammatory properties, depression relief, and neurological conditions such as epilepsy and Alzheimer's.



